First Class Tips About Does Capacitor Polarity Matter

Capacitor Polarity
1. Understanding Capacitor Fundamentals
So, you're tinkering with electronics, maybe building a cool gadget or repairing something, and you've stumbled upon the question: "Does capacitor polarity matter?" The short answer is a resounding YES! But, like most things in electronics, it's not quite that simple. Let's dive in and explore why getting the polarity right is crucial, and what happens if you don't.
Think of a capacitor like a tiny rechargeable battery, but instead of storing energy chemically, it stores it electrostatically. Theyre used in all sorts of devices, from smoothing out power supplies to timing circuits. Different types exist, each with its own characteristics, but the most important distinction for our discussion is whether they're polarized or non-polarized.
Polarized capacitors, like electrolytic and tantalum capacitors, have a designated positive (+) and negative (-) terminal. These capacitors are built in such a way that they must be connected with the correct orientation in a circuit. Non-polarized capacitors, such as ceramic and film capacitors, don't have a specific polarity and can be connected either way.
Why the fuss about polarity, then? It all comes down to their internal construction. Polarized capacitors use a chemical process to create a very thin insulating layer, which allows them to store a lot of charge in a small space. Reversing the polarity can disrupt this chemical process, leading to some rather dramatic (and potentially dangerous) consequences. Imagine trying to force water uphill — it's just not designed to work that way!
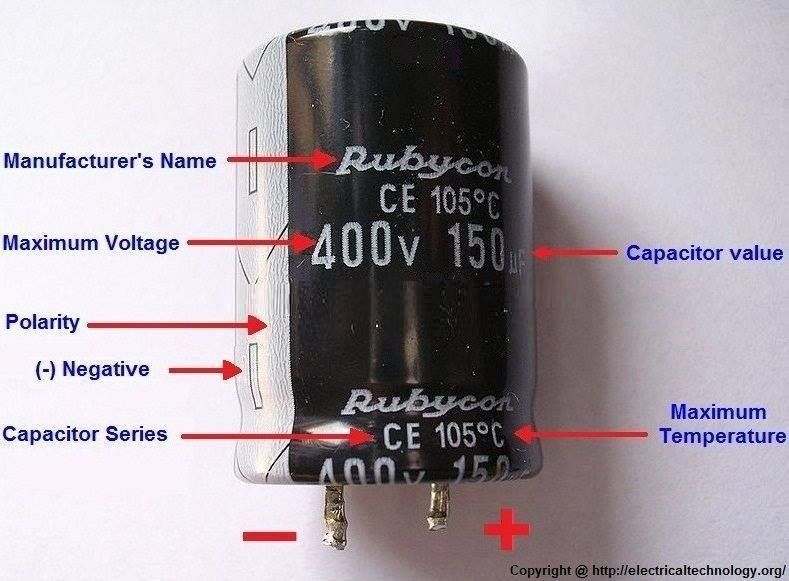
Capacitor Polarity What You Need To Know
Polarized vs. Non-Polarized
2. Identifying the Players
Okay, so we know polarity matters for some capacitors, but how do you tell the difference? Polarized capacitors are usually clearly marked with a stripe indicating the negative (-) terminal. Sometimes, you'll also see a "+" sign near the positive terminal, but the negative marking is the more common indicator. Electrolytic capacitors are generally cylindrical, while tantalum capacitors are often teardrop-shaped.
Non-polarized capacitors, on the other hand, typically don't have any polarity markings. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but the lack of a clear positive or negative indicator is your main clue. Ceramic capacitors are often small and disc-shaped, while film capacitors can be rectangular or cylindrical.
If you're ever unsure, always consult the datasheet for the specific capacitor you're using. The datasheet will provide all the necessary information, including the capacitor's polarity, voltage rating, and other important specifications. It's like reading the instruction manual before assembling furniture — it can save you a lot of headaches (and potentially broken furniture... or capacitors!).
A simple visual inspection usually solves the issue, but datasheets and parts databases (like those available from major electronic component distributors) offer a sure method of identifying the components and understanding their proper use within your projects. Always err on the side of caution! A few minutes of research beats a face full of electrolyte.

Understanding Capacitor Polarity Unveiling Its Significance In
The Perils of Reversing Polarity
3. What Happens When Things Go Wrong?
So, what happens if you accidentally connect a polarized capacitor backward? Well, the best-case scenario is that the circuit simply doesn't work. The capacitor won't charge or discharge properly, and the intended function of the circuit will be compromised. But that's the best case. Things can get much worse.
In more severe cases, reversing the polarity can cause the capacitor to overheat and potentially explode. Yes, explode! This is because the reversed voltage causes the insulating layer inside the capacitor to break down, leading to a short circuit. The rapid discharge of energy generates heat, and if enough heat is generated, the capacitor can rupture, sending electrolytic fluid and capacitor shrapnel flying. It's not pretty, and it can be dangerous.
Even if the capacitor doesn't explode, it can still be damaged and rendered useless. The reversed voltage can permanently alter the internal structure of the capacitor, degrading its performance and reducing its lifespan. So, even if it seems to work after being reversed, it's best to replace it to avoid future problems.
The severity of the consequences depends on several factors, including the voltage applied, the capacitance value, and the type of capacitor. High-voltage capacitors are generally more dangerous when reversed, as they store more energy. However, even low-voltage capacitors can explode if the conditions are right. So, it's always best to exercise caution and double-check your connections before applying power.

Capacitor Polarity, Nonpolarized And Polarized
Protecting Yourself and Your Circuits
4. Best Practices and Safety Tips
Now that you know the potential dangers of reversing capacitor polarity, let's talk about how to avoid it. The first and most important step is to always double-check your connections before applying power. Pay close attention to the polarity markings on the capacitor and the circuit board. Use a multimeter to verify the voltage polarity at the capacitor's terminals.
When working with polarized capacitors, it's also a good idea to use a current-limiting resistor in series with the capacitor during testing. This will help to limit the current flow if the capacitor is connected backward, preventing it from overheating and exploding. Think of it as a safety net for your circuit.
Another important precaution is to use capacitors with a voltage rating that is higher than the expected voltage in the circuit. This provides a safety margin and helps to prevent the capacitor from being overstressed. It's like wearing a seatbelt — it's better to be safe than sorry.
Finally, always wear safety glasses when working with electronics, especially when testing circuits with potentially explosive components. This will protect your eyes from flying debris in the event of a capacitor failure. Remember, safety first! A little bit of precaution can go a long way in preventing accidents and ensuring a safe and enjoyable electronics hobby.

Beyond Polarity
5. Voltage Ratings and More
While polarity is a critical factor, it's not the only thing to keep in mind when working with capacitors. Voltage rating is another important specification to consider. The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage that the capacitor can safely withstand. Exceeding this voltage can damage the capacitor and potentially cause it to fail. Always choose a capacitor with a voltage rating that is higher than the expected voltage in the circuit, just as we discussed before in the protecting yourself and your circuits topic.
Capacitance value is another key parameter. The capacitance value determines the amount of charge that the capacitor can store. This value is typically measured in Farads (F) or microfarads (F). Choosing the correct capacitance value is essential for proper circuit operation. Too little capacitance can result in insufficient energy storage, while too much capacitance can cause instability or other problems. Its like trying to choose the right size of container for a specific amount of liquid — you need the right fit.
Also, consider the temperature rating. Capacitors are affected by temperature and operating them above or below the specified temperature rating can significantly reduce their lifespan and impact their performance. Always check the application specifications.
In conclusion, while "does capacitor polarity matter" might seem like a simple question, the answer is a resounding yes! Understanding the different types of capacitors, their polarity markings, and the potential consequences of reversing the polarity is crucial for building safe and reliable electronic circuits. By following the best practices outlined in this article, you can protect yourself and your circuits from potential damage and ensure a successful electronics project. Now go forth and conquer your electronics endeavors with confidence and caution!

Capacitor Polarity Marking The Ultimate Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
6. Your Capacitor Conundrums Answered
Got more questions about capacitor polarity? Here are a few common ones to help you out:
Q: What happens if I use a non-polarized capacitor in place of a polarized one?
A: Generally, this can work in some applications, especially if the voltage is low and the capacitance value is appropriate. However, polarized capacitors typically offer much higher capacitance values in a smaller package. Replacing a polarized capacitor with a non-polarized one might require a significantly larger (and more expensive) component.
Q: How can I test a capacitor to see if it's bad?
A: A multimeter with a capacitance setting can be used to measure the capacitor's capacitance value. Compare the measured value to the capacitor's specified value. A significant deviation indicates a potentially faulty capacitor. You can also test for shorts or excessive leakage with a multimeter. More advanced testers can assess equivalent series resistance (ESR), which is a good indicator of capacitor health.
Q: I reversed the polarity on a capacitor briefly, but it didn't explode. Is it still okay to use?
A: Even if it didn't explode, it's likely been damaged. The internal structure may have been compromised, potentially affecting its performance and lifespan. It's always best to replace it to avoid future problems.