Casual Tips About Is 120 Volts Low Voltage

Understanding Voltage
1. What Does Voltage Really Mean?
Alright, let's talk about voltage. You might hear the term thrown around, especially if you're tinkering with electronics or just trying to figure out why your phone charger says "120V". But what does it actually mean? Think of voltage like water pressure in a pipe. The higher the pressure (voltage), the more "oomph" it has to push electricity (water) through the wires (pipes). Without enough voltage, your appliances won't work correctly, or maybe not at all. It's a pretty fundamental concept to grasping how electricity powers our lives.
Now, before we dive into whether 120 volts is considered "low voltage," it's important to realize that voltage isn't an absolute scale. What's considered low in one situation might be perfectly normal, or even high, in another. It's all relative to the application. For example, the voltage in your car's electrical system is typically around 12 volts, which is fine for powering lights and the radio, but wouldn't be enough to run your refrigerator. Context, my friends, is key!
And don't forget the terminology! We often loosely use terms like "voltage" when we really mean "voltage level." It's like saying "temperature" when you mean "a hot temperature." Getting the lingo right helps prevent confusion and makes you sound like you know what you're talking about. Nobody wants to be the person asking, "Is this uh voltage high?" while everyone else nods knowingly.
So, keep that water pressure analogy in mind as we move forward. Voltage is the force that gets the electrical current flowing, and its "height" is crucial for making our gadgets do their thing. Next up, we'll look at some voltage categories, including what exactly constitutes low voltage.

Buy ZUCKEO 120W Low Voltage Transformer Outdoor Landscape Lighting
Is 120 Volts "Low Voltage"? The Definitive Answer (Maybe)
2. Defining "Low Voltage" — It's Complicated
Okay, buckle up. This is where things get slightly... nuanced. Officially defining "low voltage" isn't as straightforward as you might think. Different standards bodies and electrical codes have different thresholds. For example, the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the US typically considers anything up to 600 volts to be low voltage. So, technically, 120 volts definitely falls into that category. However, in other contexts, such as industrial settings or with certain electrical certifications, the definition might be different.
Think of it like the speed limit. The speed limit on the highway is different than the speed limit in a school zone. Both are "speed limits," but they apply to different situations. It's the same with "low voltage." The definition depends on who you're talking to and what they're regulating. Generally, 120 volts is considered low voltage from a safety perspective and is commonly used in residential settings.
Now, just because 120 volts is considered low voltage doesn't mean it's harmless. Electricity, even at relatively low voltages, can still be dangerous if you don't treat it with respect. Always follow safety precautions when working with electricity, no matter how "low" the voltage is supposed to be. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and, if you're not comfortable, call a qualified electrician. Better safe than sorry!
Ultimately, whether 120 volts is "low voltage" depends on who you ask. But in most everyday situations, especially in homes, it definitely qualifies. Next, well explore the applications of 120 volts in our homes.
Standard And Common Voltage Levels In The US CA NEC
Where You'll Find 120 Volts in Your Home
3. The Backbone of Your Household Power
Chances are, you're surrounded by 120-volt electricity right now. It's the standard voltage for most household outlets in North America. It powers your lamps, your TV, your coffee maker, your phone charger — pretty much anything that plugs into a regular wall socket. So, if you live in a standard North American home, 120 volts is the unsung hero of your daily routine.
Ever wonder why some appliances need those chunky adapters? Well, often it's because they require a different voltage than the standard 120 volts. Some appliances, like large air conditioners or electric stoves, use 240 volts, which requires a special outlet. These higher-voltage appliances need more "oomph" to operate, hence the higher voltage. But for the vast majority of your smaller appliances, 120 volts is what keeps them running smoothly.
It's also worth noting that even though we say "120 volts," the actual voltage can fluctuate slightly. Electrical grids aren't perfect, and the voltage can vary depending on the load on the system. But it generally stays close enough to 120 volts that your appliances work without any issues. If you're seeing significant voltage fluctuations, that could indicate a problem with your home's electrical system, and you should consult a qualified electrician.
So, next time you flip a light switch or plug in your phone, take a moment to appreciate the 120 volts humming quietly in the background. It's the power behind your connected life! Now, let's compare 120 Volts versus 240 Volts in the next section.
Difference Between 120 And 240 Volts
120 Volts vs. 240 Volts
4. Understanding the Difference and Why it Matters
We've established that 120 volts is common for smaller appliances, but what about 240 volts? The key difference lies in the amount of power they can deliver. 240 volts provides twice the electrical "pressure" as 120 volts, allowing it to power devices that require more energy to operate, such as clothes dryers, electric ovens, and some air conditioning units. These appliances need the extra "oomph" to generate heat or move heavy components.
Think of it like a garden hose. If you're watering delicate flowers, a gentle spray (120 volts) is sufficient. But if you're trying to blast mud off your car (240 volts), you need a more powerful stream. Similarly, smaller appliances can run efficiently on 120 volts, while larger appliances demand the extra power that 240 volts provides.
Another important distinction is the type of outlet required. 120-volt outlets are the standard three-prong outlets you see everywhere. 240-volt outlets are larger and have a different prong configuration, preventing you from accidentally plugging a 120-volt appliance into a 240-volt outlet (which would likely fry it). These outlets are designed specifically for high-power appliances and should only be used for their intended purpose.
Finally, remember that working with 240 volts requires extra caution. Because it delivers more power, the risk of electric shock is higher. Always follow proper safety procedures and, if you're not comfortable, hire a qualified electrician to handle any 240-volt wiring or repairs. Your safety is paramount!
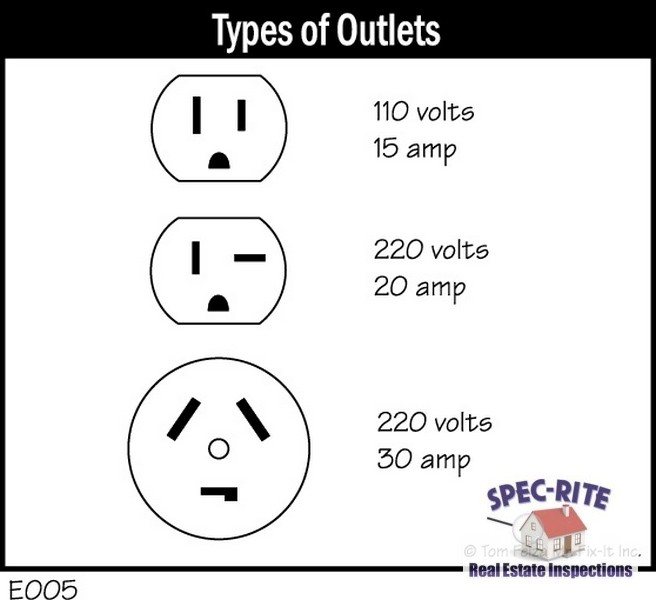

How To Tell Voltage Of Outlet
Safety First! Handling 120 Volts Responsibly
5. Respect the Power, Even at Lower Voltages
Even though 120 volts is considered low voltage, it's crucial to remember that electricity can be dangerous at any voltage. Never underestimate the power of electricity, and always treat it with respect. Simple precautions can make a huge difference in preventing accidents and ensuring your safety.
One of the most important things you can do is to regularly inspect your electrical cords and outlets for any signs of damage. Frayed cords, cracked insulation, or loose outlets can all create a safety hazard. Replace any damaged components immediately. It's a small investment that can prevent a potentially serious electric shock or even a fire.
Another essential tip is to avoid overloading your circuits. Plugging too many appliances into a single outlet can draw more current than the circuit is designed to handle, which can cause the circuit breaker to trip or even start a fire. Use power strips with built-in surge protection to protect your devices and avoid overloading the circuit.
Finally, never attempt electrical repairs unless you're qualified and comfortable doing so. Electricity is not something to mess around with. If you're not sure what you're doing, hire a qualified electrician. It's always better to be safe than sorry, especially when it comes to electricity. Now that you have a solid understanding of 120-volt power, lets look at some FAQs to solidify your knowledge.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Burning Voltage Questions Answered
We've covered a lot of ground, so let's address some common questions about 120 volts and low voltage in general.
Q: Is it safe to touch a 120-volt wire?A: Absolutely not! Even though 120 volts is considered low voltage, it can still deliver a dangerous and potentially fatal electric shock. Never touch bare wires or any exposed electrical components.
Q: Can I use a 240-volt appliance in a 120-volt outlet?A: No, you cannot. 240-volt appliances require a higher voltage to operate and a different type of outlet. Plugging a 240-volt appliance into a 120-volt outlet will likely damage the appliance and could create a safety hazard.
Q: What does it mean when a circuit breaker trips?A: A circuit breaker trips when the circuit is overloaded with too much current. This is a safety mechanism to prevent overheating and potential fires. If your circuit breaker trips frequently, it could indicate a problem with your electrical system that needs to be addressed.