Marvelous Tips About Which Motor Is Better, AC Or DC

AC vs. DC Motors
1. Understanding the Basics
So, you're pondering the age-old question: Which motor reigns supreme, AC or DC? It's a bit like asking if cats or dogs are better. Both have their strengths, their weaknesses, and dedicated fan clubs. The "better" choice really depends on what you need it to do. Before we dive into the details, let's untangle what AC and DC actually mean.
Think of AC (Alternating Current) as the electricity that flows through your house, powering your lights, TV, and that all-important coffee maker. It constantly changes direction, hence the "alternating" part. DC (Direct Current), on the other hand, flows in one direction only. Batteries are the quintessential source of DC power. Imagine the steady stream from a flashlight battery — that's DC in action.
At its core, a motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Both AC and DC motors achieve this, but through slightly different mechanisms. DC motors generally use brushes and a commutator to create motion, while AC motors, especially induction motors, rely on the magnetic field produced by the alternating current to spin the rotor. The difference in construction impacts things like speed control, efficiency, and maintenance.
Now, you might be thinking, "Okay, I get the basic electricity lesson, but how does this translate to actual motors?" Well, get ready, because we're about to explore the exciting world of motor applications!
Delving Deeper
2. Where Do They Shine?
DC motors often get the nod where variable speed control is crucial. Think about a toy train set — you can easily adjust the speed using a DC power supply. Electric vehicles also rely heavily on DC motors (although AC motors are becoming more common in EVs). The ability to precisely control the motor speed and torque makes DC motors ideal for these applications.
On the other hand, AC motors are workhorses in applications where constant speed and high power are needed. They're prevalent in industrial machinery, pumps, fans, and compressors. Because they are generally simpler in design (especially induction motors), they tend to be more reliable and require less maintenance. That's why you'll find them in everything from washing machines to large-scale manufacturing equipment.
Imagine a massive factory floor. You'll likely find countless AC motors tirelessly powering conveyor belts and machinery. These motors are built for endurance and efficiency, making them essential for keeping things humming along.
One important aspect is power availability. Since most homes and businesses use AC power, AC motors can be directly connected to the grid. DC motors, conversely, typically require a power converter to transform AC to DC if they are running from standard wall outlets.

What Is The Difference Between An AC And DC Motor?, 52 OFF
Pros and Cons
3. Weighing the Options
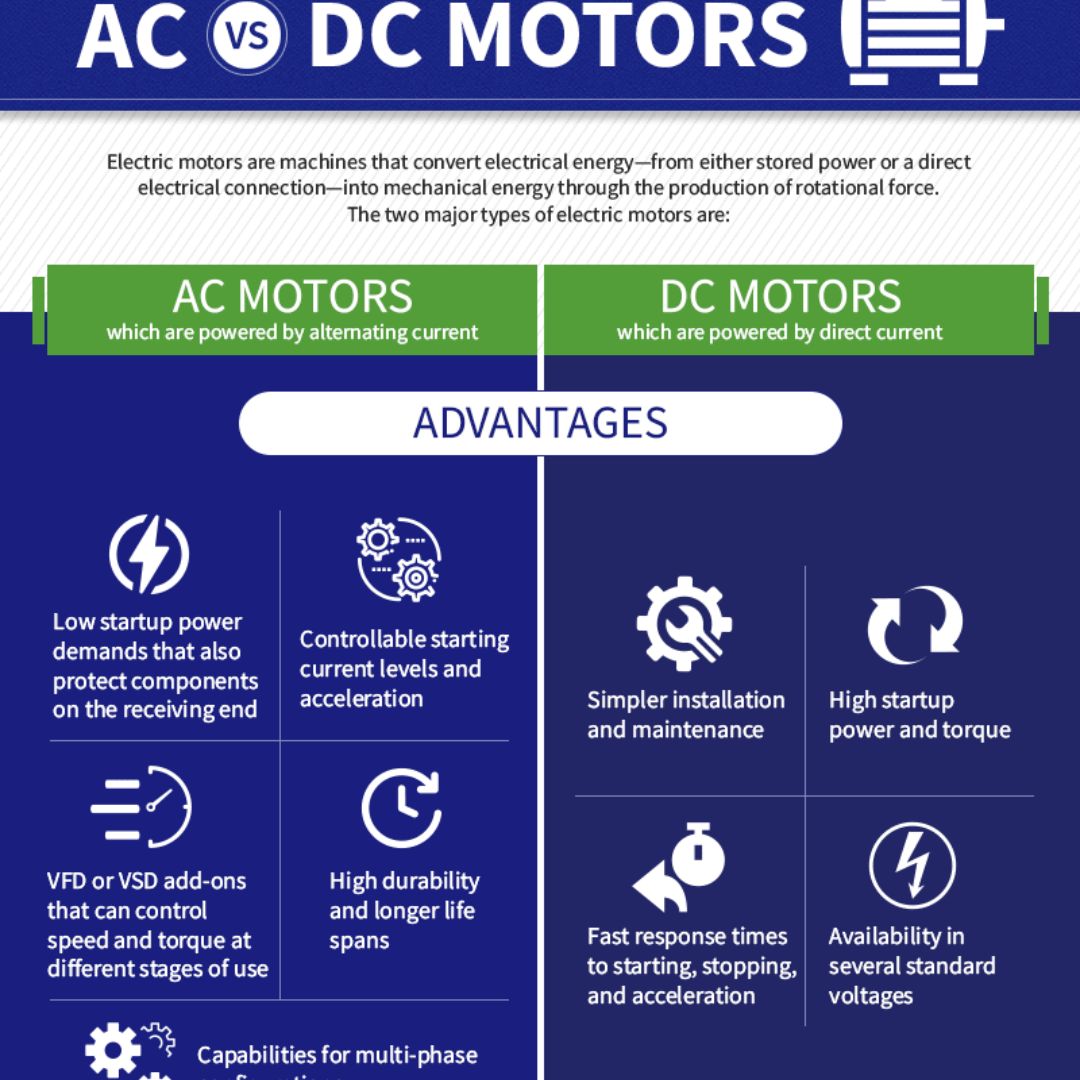
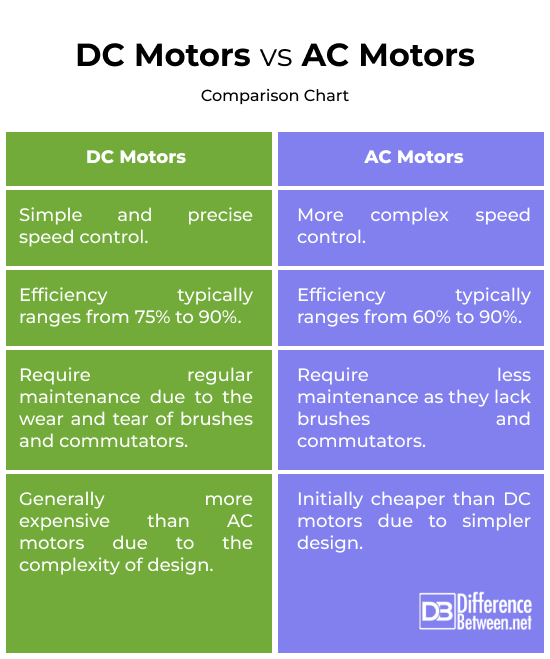
Let's get down to the nitty-gritty (oops! almost slipped up there!). It's useful to have a more structured overview. DC motors are known for their excellent starting torque and speed control, which makes them great for applications needing fine adjustments. However, they tend to be less efficient, more prone to wear and tear (due to those brushes), and sometimes noisier.
AC motors, especially induction motors, are known for their simplicity, robustness, and efficiency. The lack of brushes means less maintenance and longer lifespans. However, their speed control can be more complex and they might not provide the same level of starting torque as a DC motor. Also, some AC motors have constant speed depending on the line frequency of electricity powering it.
Consider the environment. DC motors can sometimes generate sparks from the brushes, which might be a concern in environments with flammable materials. AC motors, particularly those without brushes, are generally safer in such settings. This factor alone can be a significant deciding point in some industrial application.
Ultimately, the best choice boils down to your specific needs. Thinking about the application — power requirements, size and space constraints, and maintenance considerations are important.
The Future of Motors
4. Innovations and Trends
The motor world isn't standing still! We're seeing exciting advancements in both AC and DC motor technology. Brushless DC motors (BLDC) are gaining popularity, combining the speed control advantages of DC motors with the reliability and efficiency of AC motors. They eliminate the need for brushes, resulting in longer lifespans and reduced maintenance. As power electronics improve and become cheaper, this becomes more and more cost-effective.
Another trend is the increasing use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) with AC motors. VFDs allow you to control the speed and torque of AC motors with greater precision, making them suitable for a wider range of applications. This also increases overall efficiency, leading to energy savings and lower operating costs.
Energy efficiency is also a major driver of innovation. Manufacturers are constantly striving to develop more efficient motors that consume less power and reduce environmental impact. This includes improvements in motor design, materials, and control algorithms. Some new motors are able to recycle the energy when the motor is slowing down, creating more efficiency.
So, what does all this mean? It means the future of motors is bright, with a focus on efficiency, control, and sustainability. Whether you're Team AC or Team DC, there's plenty to look forward to!
DC Motors Vs. AC Difference Between
Making the Right Choice
5. Practical Tips
Okay, time for some real-world advice. Before you run out and buy a motor, ask yourself these questions: What will the motor be used for? What are the power requirements? What is the required speed range? What space and weight constraints are there? What maintenance requirements are acceptable? What is your budget?
If you need precise speed control and high starting torque, a DC motor (or a BLDC motor) might be the way to go. If you need a reliable, efficient motor for continuous operation, an AC motor is often a better choice. Remember to factor in the cost of any necessary power converters or control systems.
Don't be afraid to consult with experts. Motor manufacturers and distributors can provide valuable advice on selecting the right motor for your specific application. They can help you compare different models, evaluate performance characteristics, and determine the best fit for your needs. Sometimes they have application specific motors for your need.
Consider future needs too. Choosing the right motor isn't just about solving your current problem. Think about whether your needs might change in the future and select a motor that can adapt to those changes. This helps you avoid unnecessary replacement costs down the road. Making sure you get the right size motor helps with all considerations.

7 Reasons Why AC Motors Are More Efficient Than DC (Explained!)
FAQ
6. Q
A: AC motors use alternating current, are generally more efficient and require less maintenance. DC motors use direct current, offer better speed control, but typically require more maintenance due to brushes.
7. Q
A: AC motors are commonly used in home appliances due to their reliability and efficiency, but some appliances needing variable speed (like blenders) might use DC motors.
8. Q
A: Brushless DC motors offer longer lifespans, higher efficiency, and less maintenance compared to traditional DC motors, making them an excellent choice in many applications where variable speed control is needed.