Neat Tips About Is WiFi Full-duplex
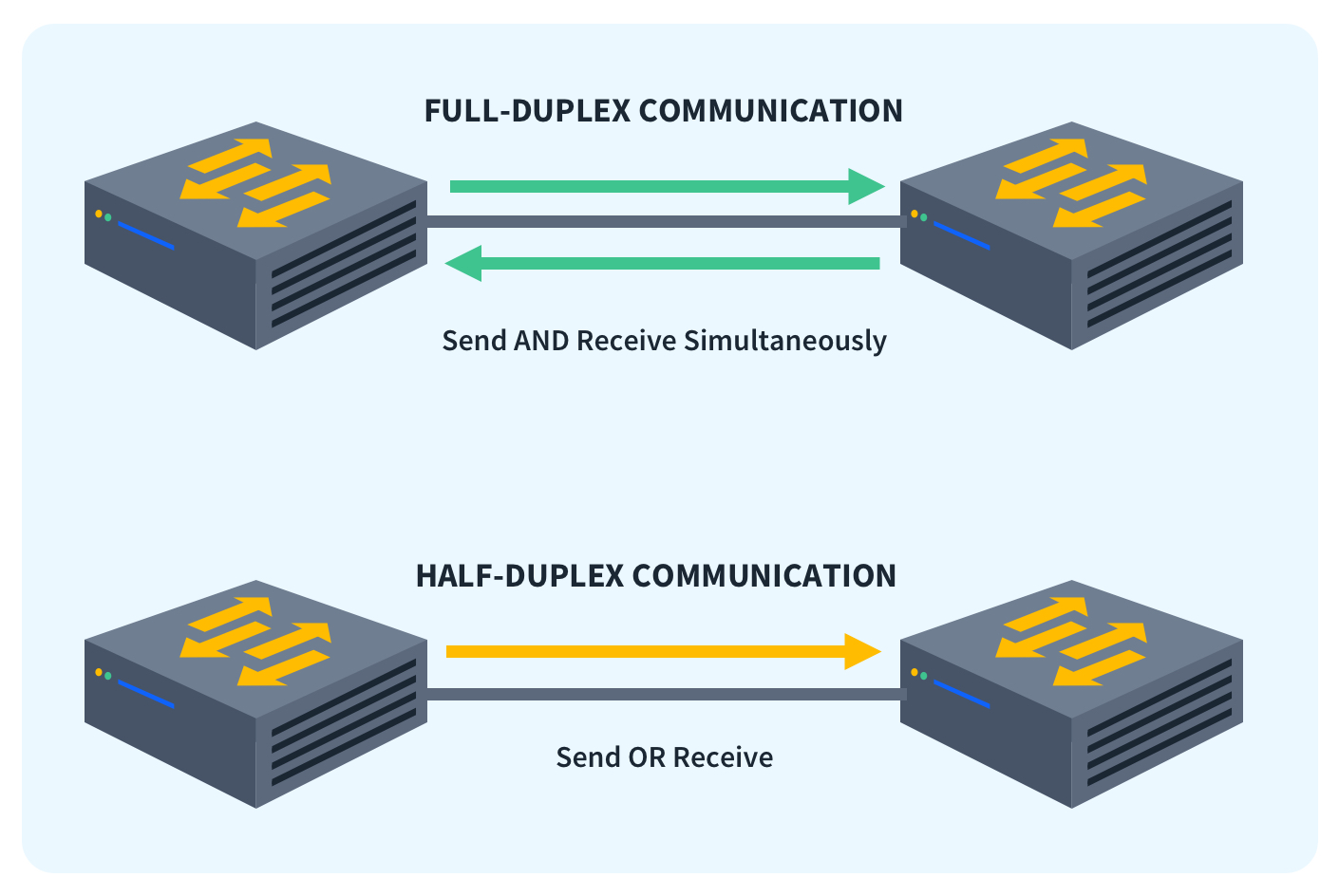
HalfDuplex Vs FullDuplex What Are The Differences?
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding the Basics of Data Transmission
Okay, let's dive into the fascinating world of WiFi and figure out if it's a one-way street or a two-way highway. The term "full-duplex" gets thrown around a lot, especially when talking about network technology, but what does it actually mean? Simply put, full-duplex communication allows devices to transmit and receive data simultaneously. Think of it like a phone call — you can talk and listen at the same time without interrupting each other. This is different from "half-duplex," where devices have to take turns sending and receiving, like using a walkie-talkie.
So, where does WiFi fit into all of this? Early WiFi standards operated more like half-duplex systems. While technically capable of sending and receiving data, they couldn't truly do both at the same time in the most efficient manner. This was due to limitations in the technology used to manage the airwaves and prevent collisions between signals. Imagine trying to have a conversation in a crowded room where everyone's shouting at once! Things would get pretty messy, pretty quickly. The early protocols had similar issues, although the technical explanations get more complex involving collision avoidance techniques.
However, technology marches on! With the advent of newer WiFi standards, like 802.11ac and especially 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), we've seen significant advancements in handling simultaneous data transmission. These improvements are not necessarily flipping the switch to fully, purely full-duplex in every sense of the word. Instead they employ sophisticated techniques to mimic full-duplex performance and improve overall network efficiency. Think of it as more like a very well-coordinated dance than everyone shouting at once.
Essentially, while earlier WiFi technologies struggled with truly simultaneous data transmission, modern advancements have moved us closer to achieving that ideal. The exact terminology might be debated by networking experts, but the practical outcome is significantly improved bi-directional data flow. Whether or not it's strictly "full-duplex" depends on how pedantic you want to get! The important thing is that your downloads and uploads are happening much more smoothly now.

Full Duplex And Half Communication
The Technicalities
2. Delving Deeper into the Technology
Alright, let's get a bit more technical. Instead of relying on the ability to send and receive signals at the very same instant on the same channel, newer WiFi standards use a combination of techniques to achieve near-full-duplex performance. One key technique is MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output). This allows a router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously by using multiple antennas to create distinct spatial streams. It's like having multiple dedicated lanes on a highway, each serving a different vehicle.
Another critical component is OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access). OFDMA divides the available bandwidth into smaller sub-channels, which can be allocated to different devices based on their needs. This allows for more efficient use of the wireless spectrum, as smaller devices don't have to wait for a large block of bandwidth to become available. Think of it as a shared resource being divided in a way that maximizes efficiency for everyone involved.
TWT (Target Wake Time) also plays a big role, although it primarily targets power saving. By negotiating a specific time for devices to wake up and exchange data, TWT reduces contention and improves overall network efficiency. The reduced contention contributes to better overall bi-directional performance as devices spend less time waiting and more time transmitting/receiving.
In essence, these technologies work together to optimize data flow, reduce latency, and increase the overall capacity of the WiFi network. They don't necessarily make WiFi purely full-duplex in the strictest theoretical sense, but they get us incredibly close to it in practice. The user experience is markedly improved with these technologies, allowing for smoother video streaming, faster downloads, and more responsive online gaming.

Practical Implications
3. The Benefits of Improved Data Transmission
So, you might be thinking, "Okay, so WiFi isn't perfectly full-duplex, but what does that even mean for me?" Well, the practical implications are actually quite significant. First and foremost, it means faster and more reliable internet speeds, especially when multiple devices are connected to your network. Remember those days of everyone in the house complaining about slow internet when someone starts streaming a movie? Those days are becoming less frequent thanks to advancements in WiFi technology.
Improved bi-directional data flow also benefits applications that require simultaneous upload and download, such as video conferencing and online gaming. Think about it — when you're on a video call, you're constantly sending video and audio data while receiving video and audio from the other participants. A more efficient WiFi connection can handle this simultaneous data flow much more smoothly, resulting in less lag and a better overall experience. Lag is the enemy of online gamers everywhere!
Furthermore, "near full-duplex" WiFi is especially beneficial in homes with lots of smart devices. From smart thermostats to smart security cameras, modern homes are becoming increasingly reliant on WiFi connectivity. The ability to handle simultaneous data transmission is crucial for ensuring that all of these devices can communicate effectively without bogging down the network. Imagine your smart fridge struggling to download recipe updates because your smart vacuum is hogging all the bandwidth! A nightmare scenario!
Ultimately, while the technical details can be complex, the benefits of improved WiFi performance are easy to appreciate. Whether you're streaming your favorite shows, working from home, or simply browsing the web, a faster and more reliable WiFi connection can make a big difference in your daily life. Thats a win in anyones book!
Debunking Myths and Addressing Misconceptions
4. Setting the Record Straight
Let's clear up some common misconceptions about WiFi and full-duplex capabilities. One common myth is that all new WiFi routers are automatically full-duplex. While newer routers generally offer better performance thanks to technologies like MU-MIMO and OFDMA, the actual level of full-duplex-like performance can vary depending on the specific model and the devices connected to it. It's always a good idea to do your research and choose a router that meets your specific needs and budget.
Another misconception is that simply upgrading your router will magically solve all your WiFi problems. While a new router can certainly improve performance, it's important to remember that other factors, such as the placement of the router, the number of devices connected to the network, and interference from other electronic devices, can also affect your WiFi speeds. Think of it like buying a fancy sports car — it won't perform optimally if you're driving on a bumpy road or stuck in traffic.
Some people also believe that wired connections are always superior to WiFi. While wired connections generally offer lower latency and more consistent speeds, modern WiFi technology has come a long way in closing the gap. For many common tasks, such as browsing the web and streaming video, the difference between wired and wireless connections is often negligible. Plus, who wants to deal with running Ethernet cables all over their house? Talk about an eyesore!
Finally, lets clarify the "near full-duplex" situation. It's not about being "fake" full-duplex. It's about leveraging existing wireless technologies in incredibly smart ways to achieve the benefits of full-duplex communication, even if the underlying mechanism isn't a pure, textbook definition of it. The result is a user experience that is vastly superior to older, half-duplex-like WiFi protocols.

Future of WiFi
5. Looking Ahead to Even Faster Speeds and Greater Efficiency
The world of WiFi technology is constantly evolving, and there are some exciting developments on the horizon. One major trend is the continued development and adoption of Wi-Fi 6E and beyond, which utilizes the 6 GHz band to provide even more bandwidth and reduce interference. This means even faster speeds and more reliable connections, especially in densely populated areas.
Another area of focus is improving the energy efficiency of WiFi devices. As more and more devices connect to the internet, the energy consumption of WiFi networks becomes a growing concern. Researchers are working on developing new techniques to reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance. Saving the planet, one byte at a time!
We're also seeing the integration of WiFi with other technologies, such as 5G and artificial intelligence. This could lead to new and innovative applications, such as seamless handoff between WiFi and cellular networks and intelligent network management that optimizes performance based on user needs. The possibilities are truly endless!
The pursuit of truly full-duplex WiFi, or at least even better approximations of it, will likely continue. It's a constant arms race between demands for higher bandwidth, more reliable connections, and smarter ways to manage the increasingly crowded airwaves. Rest assured, engineers are working hard to make your future WiFi experiences even better than they are today.